Summary
we will discuss a brief history of the Internet and how it was designed. This foundation will help you understand blockchain technology and how it builds upon the current internet protocols while enhancing and improving them. We will see how blockchain technology is changing the Internet from one of information exchange to one of value exchange. Also, we will discuss Bitcoin and how it was the first real application to showcase blockchain technology.
We will discuss some features of these new peer-to-peer networks that bring transparency and immutability to the ledger by distributing copies to all participants or nodes in the network. We will examine how this new technology is opening up new career opportunities as new talent will be necessary to build the foundation for this technology to thrive.
Blockchain is a peer-to-peer ledger system that allows peers to transact directly with each other eliminating the need for a central authority.
At its core, blockchain is a system for recording information about a transaction in a new decentralized way that makes it difficult or impossible to alter. These transactions are stored on sheets or blocks in a digital ledger that is shared among the participants of the network. Consensus on the transactions brings the peer-to-peer network into an agreement. Once the agreed-upon transaction blocks are recorded in the immutable ledger, trust becomes a fundamental component built into the system.
How it started
it started as a DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Project Agency) experiment in decentralised computing communications between two university labs in California in 1970, became the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol, INTERNET PROTOCOL SUITE (TCP/IP) developed as a standard in networking protocol or computer communication standards, and it is the backbone of today’s Internet.
With the TCP/IP protocols in place, users could link hypertext documents in an information system accessible from any node or computer using the TCP/IP protocol. The resulting information system or database is today’s World Wide Web.
With the birth of the World Wide Web, expanded usages of this new technology arose along with expanded business opportunities. Web servers, people who host and store the documents and web browsers, companies set up to help you view linked documents, help create a household need for this technology and the Internet explosion began.
Evalution of Internet
The Internet can be grouped into three distinct segments characterized by the way people interact with this new technology.
Web 1.0 - Internet of Connection
Web 2.0 - Internet of Information
Web 3.0 - Internet of Value
Web 1.0 - Internet of Connection
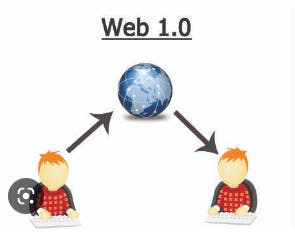
- Characteristics of Web 1.0:
Development of a host of web-based applications, which are fostered in online services, such as email.
Content from the administrator.
Managed by a central authority.
Read-only, information was “pushed” to users.
The email was the first widely adopted application on the Internet.
Web 2.0 - Internet of Information

Characteristics of Web 2.0:
User-generated content.
Read-write, individuals can interact with information.
Information became siloed.
Data became a commodity.

Web 2.0 saw emerging marketplaces that brought together unrelated buyers and sellers in a seamless low-cost way. Data became a commodity collected, siloed and sold; we were giving up our information at a frenzied pace. Websites let users generate content, social networks became part of our lives.
Web 3.0 - Internet of Value
Characteristics of Web 3.0:
Community interaction.
More connected, open, and intelligent.
Distributed ledgers or blockchain technology, smart contracts, machine learning and artificial intelligence.
Identity and information will be held by the individual, breaking data silos.

Bitcoin is the first widely accepted application for the Internet of Value (just as email was the first big application for the Internet of Information).
Bitcoin is a digital currency running on top of the Bitcoin blockchain. Bitcoin has no borders and was created as a decentralized payment system, an alternative to currencies issued by governments. Let us look at what it means to be a currency.
Purpose of currency:
Medium for exchange
Store of value over time
Accepted as a measure of worth
According to Investopedia, “Fiat currency is money a government issues that is not backed by a commodity like gold. Fiat money is backed by the government and it has value because the government says so and the citizens believe it. The Naira is an example of the Nigerian fiat currency”.
The Internet of Value represents a world where value is exchanged at the speed in which information moves today. The Internet is still the basic platform that these new technologies operate from. The new Web 3.0 browsers are being built to help you manage your cryptocurrency, keys, passwords and other blockchain features.
Apart from the government issuing Fiat, a centralized authority needs to keep track of assets. Banks, credit card companies and stockbrokers are companies that represent a centralized authority that controls your money.
Blockchain
Blockchain is a combination of several other underlying technologies that have never been combined so successfully. Here are some features that make this new technology so revolutionary.
A ledger is a collection of transactions. It is not a collection of assets. Assets are part of a transaction, but the ledger records the transaction. With a digitally distributed ledger or a blockchain, no one owns the ledger. The ledger is distributed among participants in the network, all running the same blockchain protocols. It is decentralized in that an identical copy of the ledger exists on every node/computer on the network. In 2009 with the publishing of Satoshi Nakamoto’s whitepaper “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System”, Bitcoin became the first application to leverage blockchain technology by recording the first asset transfer on a public blockchain ledger.
features that make blockchain revolutionary.
Bitcoin is transacted over the Bitcoin network, which is an open, public blockchain network. If you have an Internet connection and a Bitcoin wallet application, you can receive and send the cryptocurrency Bitcoin. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin have value because it can be proven with math. Unlike banks offering centralized services, you are responsible for your cryptocurrency.
The ledger is stored, updated, and maintained by a peer network. Nodes form the infrastructure of a blockchain network. They store, spread and preserve the blockchain data, so a blockchain exists on nodes. All nodes on a network follow the same rules of operation or protocols, but nodes have different roles. A full node contains a copy of the blockchain protocol and transaction history of the blockchain and aids in the maintenance of the blockchain. The user node interacts with the ledger. With blockchain technology, a lack of centralized authority is replaced with a peer-to-peer network.
Blockchain networks can be public or private. A public blockchain is open to anyone with an internet connection and the appropriate application. A private blockchain grants access and rights to its users before they can interact.
Blockchain ledgers are different from centralized ledgers because network participants have an agreement upon what is in the identical ledger. For the blocks to be added, all the nodes in the system come to agree as to what transactions are accurate and should be added to the chain of blocks. Since there is no central authority telling the nodes which transactions are valid, a new way to reach an agreement or come to a consensus is needed.
How each blockchain comes to a consensus is built into the protocol, they are the rules built into the code that determines how the nodes will add ledger transactions. The Bitcoin network uses a proof-of-work consensus model. This process of building agreement among a group of mutually distrusting participants is a benefit of blockchain consensus.
Cryptography and blockchain offer a secure way to prove something is authentic. Instead of relying on third-party, trust is put into cryptographic algorithms that prove the provenance and authenticity of an attestation.
Cryptography also plays a part in another powerful feature of blockchain technology, immutability. What makes blockchain incredibly powerful is that all the blocks are linked together. With the use of a cryptographic technique called hashing, the linked information is forged so that if you go back and try to change any data on any block anywhere in the shared ledger, the link with the other copies is broken in a very obvious and easy-to-determine way. With blockchain, there is no possibility of changing the data or altering the data inside the blockchain, it is permanent.
while traditional database, a system administrator oversees the ledger and can make changes.
Career opportunities in blockchain
With new technology comes new opportunities and this holds true for blockchain. As this nascent technology matures, more positions are needed to fill this increased demand. A few of these new positions are listed here:
- Entry Level and Internship Positions
Mentorship programs and internships include assisting in the designing and developing blockchain distributed ledgers based on both public and private or permissioned blockchains. With open-source, development and success depend on an active community, Working Groups and Hackathons are available for the newcomer. Skills include basic blockchain knowledge and some familiarity with basic programming languages.
Blockchain Architect
For a blockchain solution to be functional, it first needs to exist. The blockchain architect is the person or group who designs and implements the backend code of the blockchain. The blockchain architect works with blockchain engineers and technical leaders to identify the blockchain structure for specific use cases. Architects understand consensus mechanisms, cryptography systems, key management techniques and smart contract management. Qualifications include Go, Java, Javascript, or any modern programming language plus project management skills.
Blockchain Developer
Developers design, write and upload smart contracts to the blockchain. Developer design workflows that operate with blockchains and smart contracts. Responsibilities can include project design, smart contract development and implementation, front end applications design and application deployment. Skills a developer needs can include Microsoft SQL Server, Visual Studio, .NET, MVC, AJAX, SQL, C, Python, Solidity, C++, C#, Javascript, Node.js, JQuery, SOAP, REST, FTP, HTML, XML, XSLT, XCOD, Neural-networks, Regression, Agile Scrum, MYSQL. Solutions are developed for Hyperledger Fabric, Ethereum, Quorum Ripple, Corda and other distributed ledger solutions.
- Blockchain Operator
Once the blockchain solution is designed and built, operators can join to create the peer network mentioned previously. The role of operators (nodes) is to store copies of the ledger and keep their copy up to date by distributing transactions and new blocks throughout their network via peer-to-peer communications.
- Blockchain Regulator
Many businesses operate under regulations regarding how their data should be stored and processed. This is the same for blockchain solutions. Regulators rarely interact with the blockchain directly, rather oversee regulatory requirements that need to be considered in blockchain development. With governments researching Central Bank Digital Currencies, governing these blockchains will become increasingly more complex.
- Blockchain Project Managers
Project managers are the first persons in an organization who are contacted when a company wants to bring blockchain in house and adapt it to their technology platforms. Responsibilities include deciding if a blockchain solution is a good fit for a business situation. If the decision is to move forward, Project Managers would organize key players and resources needed to execute the blockchain project.
- Data Storage and Processing Managers
The blockchain provides distributed, immutable storage with built-in integrity checking, but certain limitations exist that have to be managed. Data decisions need to be made dealing with maximum capacity based on the standard block size and block rate. Policies need to address how to provide integrity verification for large amounts of data, should data be stored off-chain with a hash of the data stored on-chain. eMembers of the peer network must execute the code to remain in sync with the current state of the network. If smart contracts commonly require large amounts of processing power to complete, devices external to the peer network may be used to augment the processing power of the network.
- Blockchain Data Scientists
Blockchain has the ability to collect large amounts of data. The Blockchain Data Scientist collects, interprets, analyzes and manages data. Developing algorithms that can analyze patterns in large data sets, the data scientist provides insight into the data collected.
- Blockchain Quality Engineer
This position is responsible for ensuring quality in all areas of blockchain development, such as automation frameworks and tests, manual testing and dashboards to support mobile, web and platform engineering. A quality engineer will need to research and advise on blockchain tools and develop quality assurance (QA) automated test standards, as well as define, write and implement test automation strategies for load performance tests. Applicants may also need an engineering management MBA degree.
- Blockchain Legal Consultant or Attorney
A blockchain legal consultant is responsible for advising companies on how to structure blockchain endeavors. Advise on how to structure and govern initial coin offerings, some of which are now coming under greater regulatory scrutiny. Attorneys will also be tasked with developing legal partnerships and contracts as blockchain technology offers "smart contracts", which are self-executing based on previously agreed terms. Duties can include designing legal partnerships that would connect the crypto ecosystem with existing financial structures, and supporting various merger-and-acquisition activities, such as negotiating and drafting legal agreements and performing due diligence on blockchain projects.
- Blockchain Web Designer
A decentralized community needs to keep the community that supports it informed. When including the use of cryptocurrencies in your business and when launching blockchains, there will be a greater need for websites to inform customers what a company is offering. A blockchain web designer will need to come up with original concepts, creative graphics and "mind-blowing" user interfaces and dashboards to engage a diverse and inclusive community.
- Blockchain Consultants
Blockchain consulting companies and blockchain consultants are tasked with advising companies on designing and implementing blockchain solutions. This includes the documentation and maintenance of solutions, as well as their initial implementations.
- NFT Graphics Designer
NFT stands for a non fungible token, a special token that represents a unique ID that is linked to a piece of crypto art that cannot be replicated and is used to verify ownership of a piece. The collectable world is jumping in head first and creating non fungible tokens that represent art, music, memorializing events, newspaper articles and record releases. Designers are needed to turn these moments/media into art for the thirsty NFT market.